Fusing is a base fabric having a deposition of thermoplastic adhesive resin which can be bonded to another fabric by the application of heat and pressure.
Regardless of which fusible and machine are used, fusing is controlled by four processing components – temperature, time, pressure and cooling and these have to be accurately combined in order to achieve the optimum results.
Temperature-
There is a limited range of temperatures that are effective for each type of resin. Too high temperature causes the resin to become too viscous, which could result in the resin being forced through the right side of the cloth. If the temperature is too low, the resin is not sufficiently viscous to disburse into the top cloth. In general, resin-melt temperatures range from 1300 to 1600 C and the best results will normally occur within ± 70C of the temperature specified by the manufacturer of the fusible.
Time-
The only time element of any value during the fusing process is when the top cloth and fusible are under pressure in the heating zone of the machine. This time cycle for a particular fusible is determined by –
a. Whether the fusible has a high or low melt resin.
b. If a light or heavy substrate is being used.
c. The nature of the top cloth being used, i.e. thick or thin, dense or open.
Manufacturers of fusible supply data sheets which give the time cycle for each fusible, and this refers to the actual fusing stage only.
Pressure-
When the resin is viscous, pressure is applied to the top cloth and fusible assembly to ensure that –
a. Full contact is made between the top cloths and fusible.
b. Heat transfer is at the optimum level.
c. There is an even penetration of the viscous resin into the fibres of the top cloth.
Most fusing machines use two steel rollers or pressure plates to create pressure, but a flexible pressure system has been developed which automatically adapts itself to variations in the thickness of the assembly being fused, whilst maintaining an even pressure over the entirely assembly.
Cooling-
Enforced cooling is used so that the fused assemblies can be handled immediately after fusing. Cooling can be induced by various systems, including water-cooled plates, compressed air circulation and vacuum. Rapidly cooling the fused assemblies to 300 to – 350 C makes a higher level of productivity than if operators have to wait for the assemblies to cool naturally.
The fusing process produces what is, in effect, the foundation of a garment and the best results can only be achieved when there is an accurate and continual control of the four processing components.
Elements which should be checked before deciding any machinery –
- Capacity-
- Amount of production is required
- Loading-
- Feeding into the machine
- Instrumentation-
- The instruments attached to the machine are reliable and accurate to the standards required by the industry
- Cooling-
- Is it effective and what time is it taken by the machine for effective cooling
- Take-off-
- Whether manual or automatic
- Safety –
- Devices to prevent accidents and to stop the entry of wrongly positioned components.
- Space and location-
- Space is required by the machine
- Maintenance-
- Maintenance training and time period of maintenance
- Cost-
- Comparison between different machines
- Pay back-
- Payback time in relation to the total investment required
Three basic types are –
- Steam press
- Flat bed press
- Conveyor belt press
Each type of machine has its own range of capabilities.
- Steam press-

Regular steam pressing machines are not designed for fusing although some fusible are produced for use on these machines. Pressing machines have some serious limitations regarding fusing including –
- Inability to reach the heat levels required by the majority of resins.
- Pressure applied all over the buck area is uneven, which restricts the machine’s use to the fusing of small parts.
- The shape and size of the bucks restrict the size of the components which can be fused.
- Most utility machines are not fitted with programmed controls, which mean that the entire process is operator controlled.
- If the resin was originally activated by steam heat, the same thing can happen when garments are pressed during their production. This situation can cause serious problems with the stability of the laminates.
Regular steam pressing machines are not the ideal medium for fusing.
- Flat bed press
Flat bed presses are purpose built fusing machines produced in a large variety of sizes and which many types of work aids. This type of press has padded top and bottom bucks with electric heating elements in one or both bucks. The bottom buck is static and the top buck is lowered to fuse the assembly whilst under pressure, and then raised after cooling. Most of these machines are fitted with timers and programmed controls and can achieve high levels of fusing quality.
 |
| Flat bed press fusing machine
Some other models do not have a built in feeding system, and prepared assemblies have to be brought to the machine by hand, generally on sheet of a thick paper. After fusing, the sheet is removed, the parts are stripped, and the sheet is prepared for another cycle. The method works as follows-
This type of presses is present in single tray or twin-tray system. Twin-tray systems are considerably more productive than those with single tray because of the time lag caused by waiting fusing cycle to end for arranging the assembly again on the sheet is considerably reduced. Another type of flat bed press is incorporated into a carousel by using three trays that successively move through the loading, fusing and cooling stations. These machines are generally sued for top fusing of shirt and blouse collar. Carousel press Observation regarding flat bed press-
|
- Conveyor belt press-
Conveyor belt presses are also called continuous machines because they can be operated without stopping for the loading and unloading of the assemblies. The conveyor belt transports the assemblies through all the processes and the belt speed is adjustable according to the time cycle required. This type of machine is available in different lengths and widths and can be fitted with automatic feeding and unloading systems. A feature of the more modern machines is a microprocessor which can be programmed to control every element of the machines operation.
This type of machine has an endless conveyer system for transporting the assemblies successfully through the heating, pressure and cooling stages. In this system, the garment is passed through a heat source simultaneously, or subsequently applying pressure.
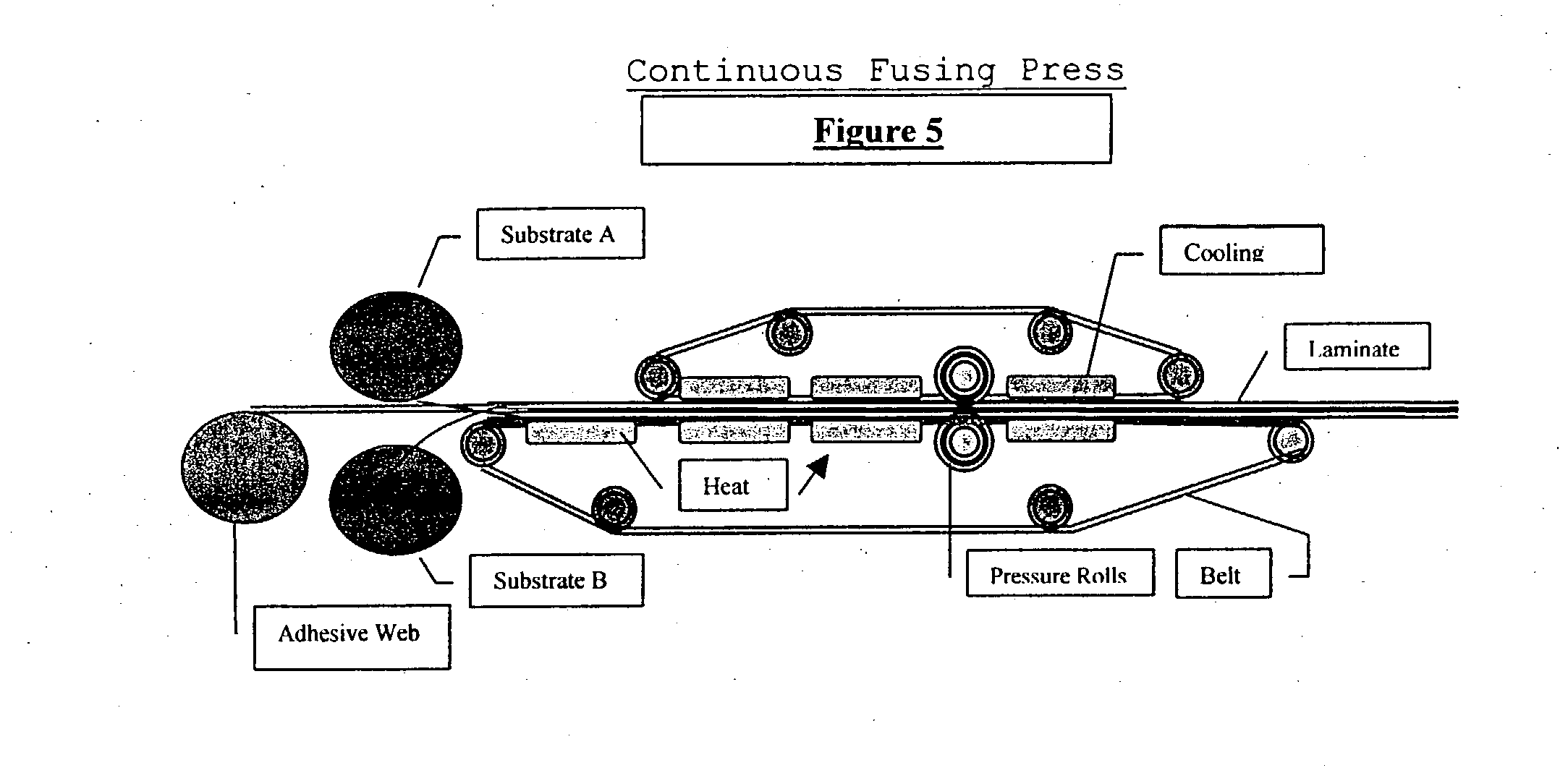
Conveyor type-
Two systems are in general use-
- End to end feed-
The parts are conveyed from the loading area at one end of the machine, via the fusing area to the take off area at the opposite end of the machine.
- Return feed-
This conveyor system is, in effect, two belts, one upper and one lower, where the lower belt is the actual conveyor of the cloth and fusible. The function of the upper belt is to ensure that both cloth and fusible are held accurately in the correct positions while being transported through the fusing process.
Heating Mechanism –
The heating systems generally used for continuous fusing presses are:
Heating Plates – These consist of two heating surfaces, positioned apart, with one above the conveyor belt and one below the conveyor belt. The lower heating element surface area is more than the upper one. Both have separate temperature control profile.
Cylinder Heating – The cylinder consists of two parts
- Inner cylinder-
- a stationary assembly in which the heating element are mounted
- Outer cylinder-
- which rotates around the inner cylinder.
This principle ensures that the heat generated by the inner core is evenly distributed all over the cylinder mantle.
Pressure Mechanism
Pressure is applied continuously and evenly, throughout the entire process once fed into the machine, but that pressure is just sufficient to only hold the fabric and fusing together and to prevent slipping. Actual pressure is applied at the outlet point, where drums put heavy pressure on just heated fusible piece.
Time Mechanism
Fusing time depends on the speed on the conveyor belt, the faster the belt runs, the shorter the time. All machines have a belt speed controller which can be adjusted to give various dwell times in the heated zone.
New developments-
The major innovation in fusing technology has been developed in recent years are-
- High frequency stabilization-
The system utilizes high frequency to create heat.
-
- Fabrics are non conductive materials and with constant voltage , no electric current can be conducted through the mistake through the stack of fabric.
- However if an electric plate is positioned over the stack and another positioned under the stack and both pieces are fed with high frequency voltage an electric field will be formed between the two plates which lead to forms dipoles of molecules of fabrics and align the in a particular direction.
- As a result of constant commutation of the electric field which force the dipoles to change their position constantly owing to permanent friction losses and thus heat generation in even manner.
- Direct stabilization-
- In this method the stabilization and reinforcement of the top cloth are achieved without the use of fusible interlinings.
- Instead the stabilization material is printed directly on the top cloth.
Principles are as follows-
A polymer paste is printed on the cloth in the form of closely spaced lines and when subjected to pressure, the lines penetrate into the cloth to about half of their thickness. After printing he parts are transported by a conveyor to the drying and curing zone.
The machine can be used for continuous fusing in case a specific type of applied reinforcement is required on the top of the coated area.
Advantages it offers are-
- The savings in fusible interlinings
- The elimination of all the processes of all the work connected with the cutting of fusible.
- The reduction of storage space and logistic problems
Suggested Machines improvement:-
- Placement of heat sensor:- Heat sensor is placed near the heating element of the machine/ heat source and not the actual applied temperature of resin-heating zone. The difference in the temperature is due to:-
- Covers over heat source such as conveyor belts, protective frames etc.
- Pressure support system
- Residual moisture content of the fabric
- The insulating properties of cloth and fusible.
- The machine environment and heat dissipation
- Quick and narrow thermostat region:- A quicker and narrow thermostat region with a variation of ±2OC will help the fusing material to work properly. The lower limit of the thermostat will be the specified ambient temperature.
- Customised heating zones:- For using polyzonal fusing, the heating element should be customised. It can be done in factories specialised in less style changing products.
- Self regulating Machine:- Before starting fusing we have to feed the spec sheet data from both fabric supplier and fusing material supplier into the machine and then machine will show the available optimum settings for the same.
Machines used in industry:-
- HKH Fusing by Veit

Advantages of HKH
- Heating System:
The heating plate guarantees exact and reliable temperature control. This ensures intensive heat transfer and a high heat capacity. - The Pressure System:
The forming pressure is hydraulically controlled and generates an even pressure distribution. - Cold Pressing Station:
The cold pressing station consists of two water-cooled pressing plates. The fused assemblies are pressed between these cooled plates, reducing temperature rapidly to stabilise the fusing effect. - Press Padding:
The well-designed padding withstands both high temperature and extreme pressure for a long and trouble-free life span. - Conveyor System:
The conveyor system consists of a top and a bottom belt, guided on both sides by chains to avoid distortion. The lower belt transports the assemblies from the loading station, through the two pressing stations, to the unloading stations. The upper belt prevents shifting with light pressure, and keeps the parts from sticking to the top plate. Both belts are manufactured from adhesiveresistant materials. - Low pressure device:
A pressure range from 2 – 10 N/cm² can be adjusted with the optional low pressure device.
- Fusing Machine FX DIAMOND 1000 / 1400 / 1400L / 1600
Manufactutrer :- Veit

- Optimal fusing results thanks to exact temperature control directly at the belt
- Consistent fusing results due to consistent pressure over the entire operating width
- Optimal adjustment of pressure system (soft, medium) and heating sequence (top, bottom) to the materials to be processed
- Perfectly designed service concept allows easy and regular cleaning of machine
- Lowest possible energy consumption due to:
separate feeding belt, no cooling of transport belt outside of machine complete encapsulation of heating units for extremely low heat loss decoupling of heating zones from machine frame
- separate feeding belt, no cooling of transport belt outside of machine
- Easy operating with new 7“ colour touch display
- Reduced wear and tear of belt edge through contact-free belt detection
- Prevention of faulty fusing through start/stopp-function in the event of a diversion from pre-set fusing parameters. This allows the operator to step in
- Consistent fusing quality due to optimized cleaning of the belts both on the inner and the outer side. Consequently, major reduction in soiling of roller and fusing material
- KCF 450 U
Manufacturer:- Welcogm
- Advantage:-
- User friendly
- Ergonomically designed to be used by one operator
- One side open
- Return cooling device
REFERENCES
- http://textileapex.blogspot.in/2014/09/fusing-process-machinery.html
- Fusing technolgy

