Spinning is a major part of the textile industry. It is a part of the manufacturing process where fiber is converted into yarn, then fabric, which undergoes finishing processes such as bleaching to become textiles.
Spinning is the twisting together of drawn out strands of fibers to form yarn, though it is colloquially used to describe the process of drawing out, inserting the twist, and winding onto cones.
In simple words, spinning is a process in which we convert fibers by passing throughout certain processes Blow Room, Carding, Drawing, and finally winding into yarns. These yarns are then wound onto cones.
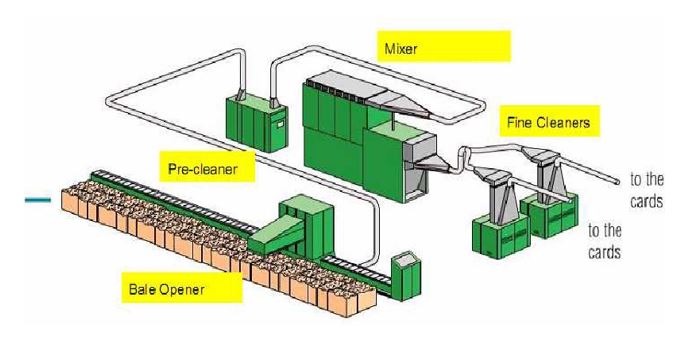
BLOW ROOM
Blow Room is the starting of spinning operation where the fiber is opened, cleaned, mixed, micro dust removed and evened.
Functions of Blow Room:
- Opening
- Opening is the first operation within the Blow Room in which the goal is high degree of openness of material with gentle treatment and a fiber loss as less as possible
- Bales of cotton are laid down uniformly in layer
- Machine called Blendomate picks up material uniformly. The parts in this machine:
- Two supporting rollers: Contain spikes used for picking up bales of cotton and evening them out
- Pressing Roller: Present in the center of the machine which evens out the cotton
- Two opening rollers: Cuts the cotton and sucks it into the machine
- Cotton is sucked into this machine and then enters all the other machines
- The size of lumps is decreased
- Mixing
- Homogeneous mixing of cotton takes place
- Blending of fiber material is an essential preliminary in the production of a yarn
- Fibers can be blended at various stages of the process
- However, the starting process is one of the most important stages for blending, since the components are still separate and therefore can be metered exactly and without dependence upon random effects
- Cotton drops on the lattice and it moves forward
- Cleaning
- Cotton contains up to 18% trash in most cases. To clean the material, it is unavoidable to remove as much fiber as much waste
- Therefore, it is necessary to measure the amount of the waste removed and its composition. As it is of high importance also called cleaning efficiency
- The cleaning efficiency always has to be optimized and not maximized, since the fiber quality as well as fiber loss is always negatively affected by maximum trash removal
- The waste is collected in a waste trolley
CARDING
Carding is a mechanical process that disentangles, cleans and intermixes fibers to produce a continuous web or sliver suitable for subsequent processing. This is achieved by passing the fibers between differentially moving surfaces covered with card clothing. It breaks up locks and unorganized clumps of fiber and then aligns the individual fibers to be parallel with each other
- Cotton is opened, trash is removed from it and sliver is formed
- The loose cotton is put in a cylinder and then made to enter the carding machine, which is known as DOPHER
Objectives of Carding:
- Open tuft into individual fiber
- Cleaning of cotton by removal of trash and dust
- Elimination of neps and short fibers
- Straightening of fibers
- Sliver formation
- Sliver gets collected in a moving cylinder
DRAWING
- The input sliver is kept in stationary cylinders
- After passing through the draw frame, the combined sliver is collected in moving cylinders
- 6 slivers are converted into a single sliver, hence called unit 6 sliver
- Wider the draw frame, more even is the sliver formed
Objectives of Draw Frame:
- Evenness of sliver
- Gradual parallelisation of fibers
- Homogeneous blending
- Dust removal from slivers
- Hooks in fibers get straightened
- To even out weight per unit length, which is achieved by the Autoleveller
WINDING
The creation of large yarn packages that can be easily unwound, is called winding. This makes using the yarn on subsequent machines easier and more economical.
Objectives of Winding:
- To convert sliver into twisted yarn
- To wind yarn onto the package
- The machine is gear driven which fixes the length of the thread (22,000 yards)
- The machine automatically stops if the sliver(input) breaks or when the fixed length is achieved
An Article By: